Taking Kubernetes security scanning to the next level with Starboard
Background
After previously looking at trivy and kube-bench as a standalone benchmarking tool, I then began experimenting with Starboard, an integrated suite of Kubernetes security tools, which includes trivy, kube-bench, and a couple of other useful tools.
The purpose of this post is to document how I install and run Starboard CLI on Kubernetes clusters in my home lab.
Install
Before we do anything, let’s make a new directory to put our installation files in.
mkdir starboard
cd starboard/
To install Starboard, download the latest release from the archive using wget and then extract it.
wget https://github.com/aquasecurity/starboard/releases/download/v0.15.8/starboard_linux_x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf starboard_linux_x86_64.tar.gz
Next, move the Starboard binary into a $PATH location so that you can run starboard commands from the CLI.
sudo mv ./starboard /usr/local/bin/starboard
Check everything’s working as expected by running starboard help.
Lastly, initialise Starboard by running starboard install. This one-time command creates a starboard namespace and sends custom security resource definitions to the Kubernetes API.
Scanning workloads
Vulnerability Scans
Starboard utilises Trivy to perform vulnerability scans.
To run a vulnerability scan against a specific pod:
starboard scan vulnerabilityreports pod/[pod name]
… or all pods in a deployment:
starboard scan vulnerabilityreports deployment/[deployment name]
Once the scan has completed run the following command to retrieve the latest results for the pod / deployment you specify:
starboard get vulnerabilityreports deployment/[deployment name] -o yaml
If the scanned deployment contains multiple containers, you can use the --container flag to retrieve the results for a specific container:
starboard get vulnerabilityreports deployment/[deployment name] --container [container name] -o yaml
CIS benchmark scans
Starboard incorporates kube-bench to run CIS benchmark scans of clusters. To start a scan:
starboard scan ciskubebenchreports
To retrieve kube-bench reports:
kubectl get ciskubebenchreports -o wide
kube-hunter scans
We can take our vulnerability scanning a step further by using kube-hunter to hunt for vulnerabilities in a cluster. Running kube-hunter is as simple as:
starboard scan kubehunterreports
Like the kube-bench results, Starboard stores the output from kube-hunter as a CRD that we can call with kubectl get:
kubectl get kubehunterreports -o wide
Generating HTML reports
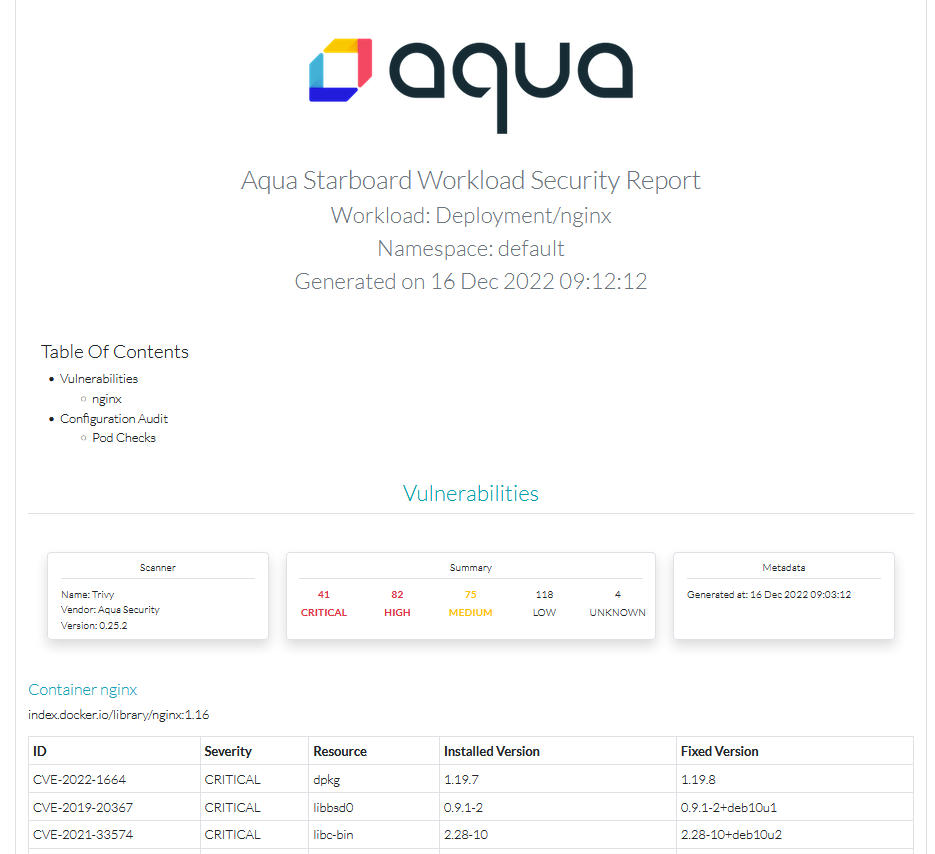
Outputting yaml to the CLI is handy for quick checks, but it’s possible to make the reports more presentable by generating them in an HTML format:
starboard report deployment/[deployment name] > [report name].html
If you’re SSH’d into the server you’re running Starboard on, you can view the reports by copying them to your local machine or by launching a temporary webserver on the server using the following command:
python3 -m http.server 8001
The following is an example of the generated report format.