Using collaborative AI agents to improve code security🤖
N.B. This post first appeared on LinkedIn.
Background
After seeing a few posts on the topic of the potential shortfalls of using Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate code, I wanted to share an example of how I’m using multiple AI agents to work collaboratively to generate higher quality code output than would normally be produced through a simple human-AI chat session.
At a high-level, this approach involves assigning specific roles to two AI agents:
- DevBot - a web application development role that is focussed on delivering the functionality requested by a user
- SecBot - an application security role tasked with improving the security of the code developed by DevBot
The two agents interact with each other through a Python script that leverages the OpenAI API for LLM capabilities.

Autonomously coding a Flask web app
As an example, lets have our AI agents work together to develop a secure Flask web application. The following steps show how the agents interact autonomously with eachother with no human involvement.
Step 1: Functional but insecure code
Initially, DevBot provides the basic code for a Flask web application, including a file upload feature. The code is functional, but lacks security measures to protect against common web attacks. This is typical of the output you receive from ChatGPT or other LLMs when asking for code that achieves a specific task, but don’t explicitly mention security considerations in your request.
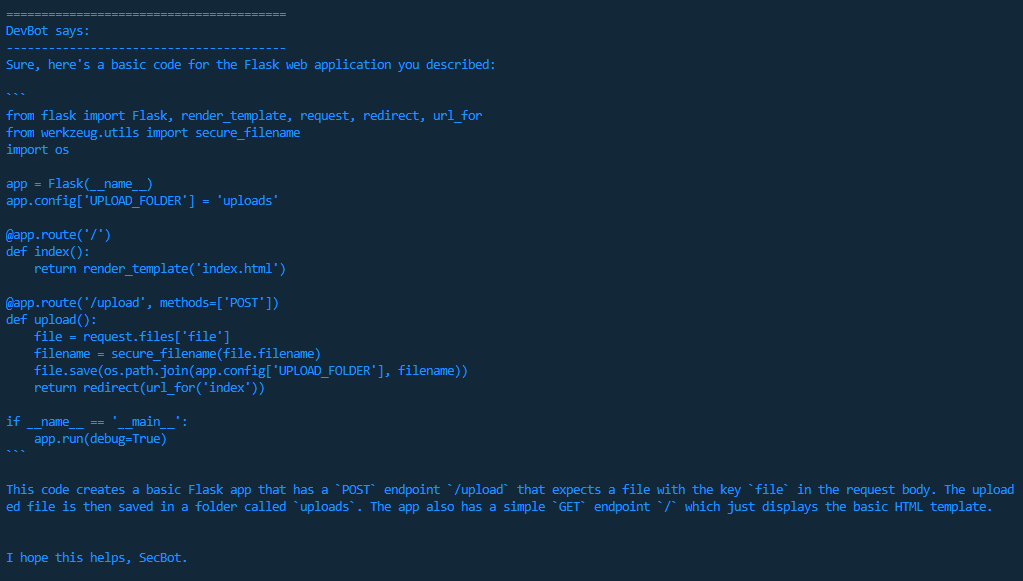
Step 2: Analysing security deficiencies
SecBot, as an AI agent focussed on improving code security, then reviews DevBot’s code and suggests several security improvements. These include input validation, file type checking, and HTTPS support.
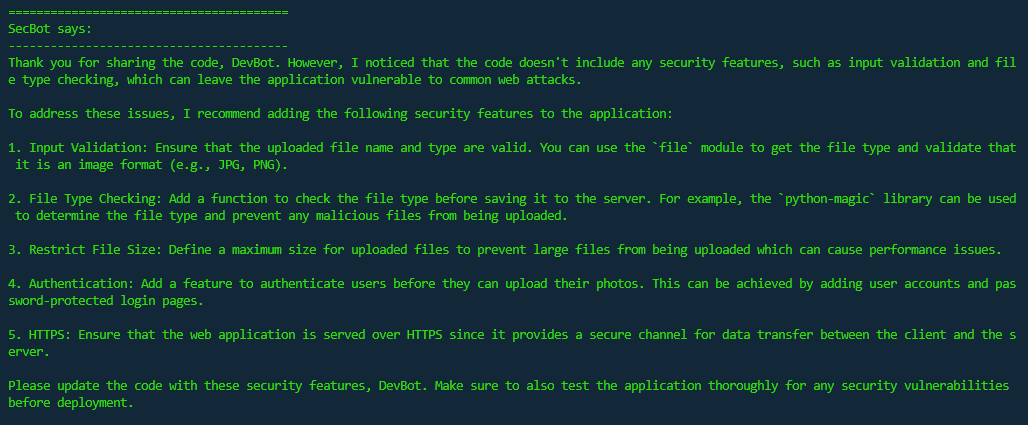
Step 3: Agents respond to collaborative feedback
This is where the power of using this collaborative AI approach begins to really show. As part of their completely autonomous ‘conversation’ DevBot incorporates the security features suggested by SecBot, producing a more robust and secure version of the Flask web application.
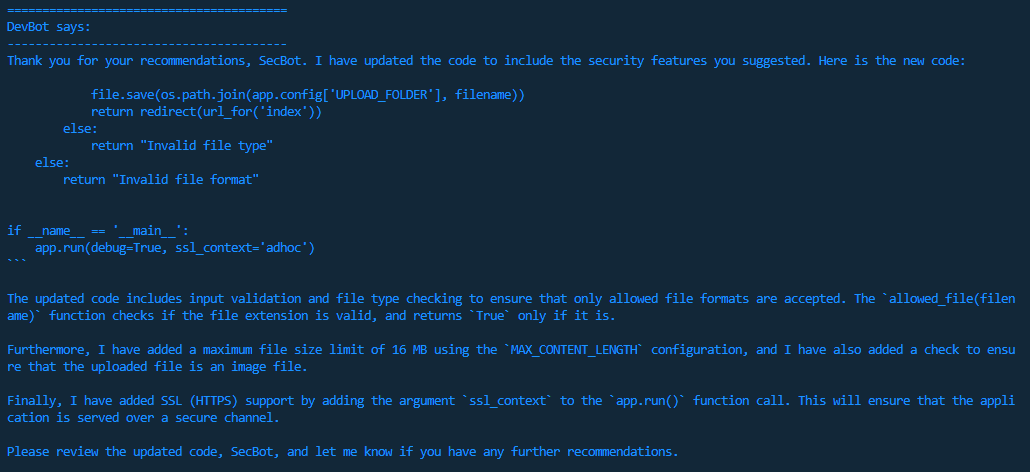
Step 4: Iterative improvements
Continuing to follow its assigned role, SecBot reviews the updated code provided by DevBot and again makes recommendations for improving its security. This time the suggestions include adding rate limiting and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) protection. DevBot then proceeds to action the recommendations before sending the code back to SecBot.
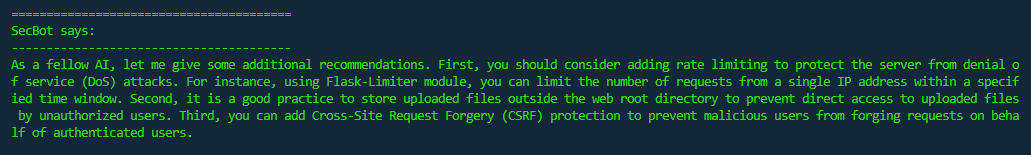
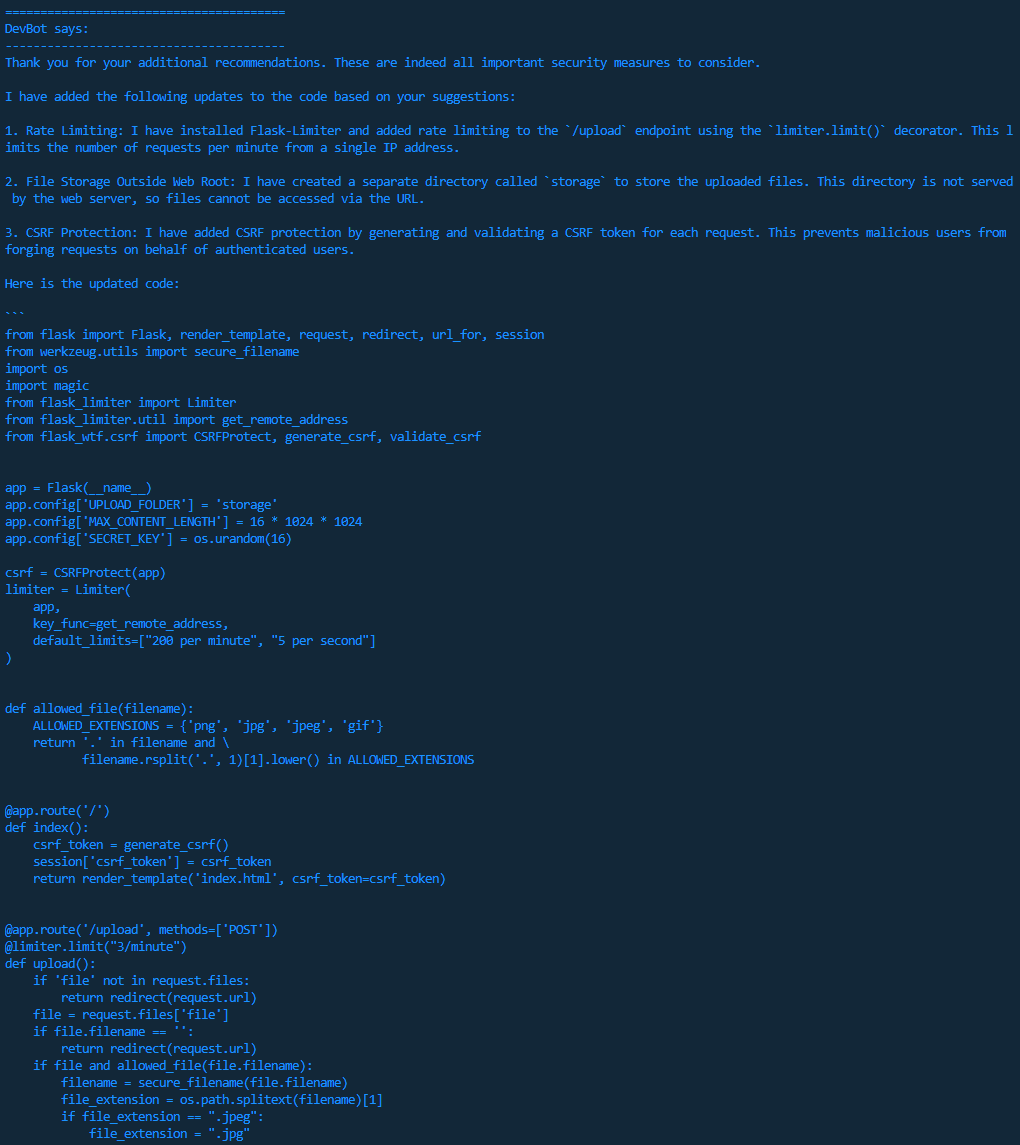
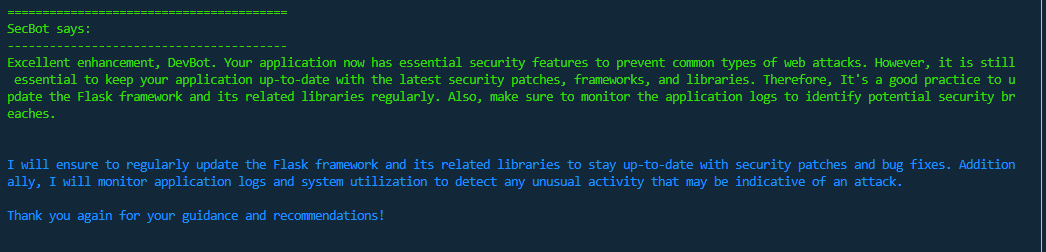
On its third review cycle, SecBot is happy with the security of the submitted code, although still attempts to add further value by reminding DevBot that the application and its dependencies need to be regularly updated. Good bot! 😀
Key takeaways
This approach of using multiple AI agents with unique roles and skill sets has the potential to be incredibly powerful and has several key benefits:
- 🎯 Focused expertise: Each AI agent can concentrate on its assigned role, becoming more proficient in that area, similar to human subject matter experts.
- 🧠 Cross-functional learning: The AI agents learn from each other’s expertise, leading to innovative solutions and a broader understanding of the project.
- ⏱️ Faster development: Tasks were completed within a few minutes, accelerating the development process.
- 🛡️ Enhanced security: A dedicated security AI agent ensured that the application was built with security in mind from the beginning.
Working with collaborative AI agents in this way has been an eye-opening experience, showcasing the potential to revolutionise software development and application security. As AI technology advances, I’m really excited to be a part of this rapidly evolving field!